In the ongoing quest for sustainability and environmental stewardship, waste management has emerged as a critical component of modern society's efforts to reduce, reuse, and recycle. Among the various stages of waste management, compression and packing play pivotal roles in optimizing space utilization, reducing transportation costs, and facilitating efficient recycling processes. One technology that has proven particularly effective in this context is the use of hot melt strap—a versatile and reliable tool that enhances waste compression and ensures efficient recycling. This article delves into the intricacies of hot melt strap, its applications in waste compression, and the broader implications for efficient recycling operations.
Understanding Hot Melt Strap
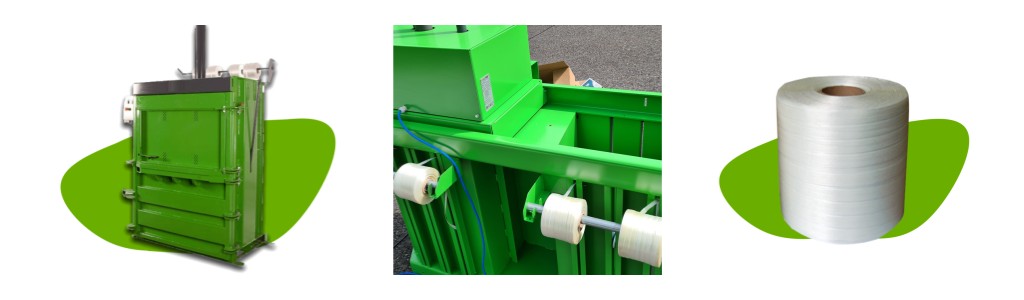
Hot melt strap is a type of packaging material that utilizes thermoplastic polymers. Unlike traditional strapping materials such as steel, polyester, or nylon, hot melt strap does not require mechanical fasteners like buckles or seals. Instead, it bonds directly to itself when heated, creating a strong, secure hold. This unique bonding mechanism makes hot melt strap particularly suitable for applications requiring high tensile strength and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature fluctuations.
The process of applying hot melt strap involves using a specialized tool that melts the adhesive layer of the strap and applies it to the package or bundle. Upon cooling, the strap solidifies, forming a tight and durable bond. This process not only simplifies the strapping operation but also minimizes the risk of strap breakage or loosening, which is crucial in waste compression scenarios where stability and security are paramount.

Applications in Waste Compression
In the realm of waste management, hot melt strap has found niche applications, particularly in waste compression and packing. Waste materials, ranging from household garbage to industrial scraps, often come in varied shapes, sizes, and consistencies. Compressing these materials into more manageable and compact forms facilitates easier handling, transportation, and recycling.
Hot melt strap excels in this role due to several key attributes:
High Tensile Strength: The ability of hot melt strap to withstand significant tensile forces ensures that compressed waste remains securely bundled, preventing shifts or spills during transportation.
Water and Moisture Resistance: Unlike some traditional strapping materials, hot melt strap maintains its integrity in the presence of moisture, making it ideal for waste streams that may contain liquids or be exposed to wet conditions.
Flexibility and Adaptability: The adjustable nature of hot melt strap allows it to conform to the contours of compressed waste, providing a snug and secure fit without damaging the material being strapped.
Ease of Application and Removal: The application process is straightforward and requires minimal training. Moreover, the strap can be easily cut and removed when the waste is ready for recycling or disposal, minimizing the risk of damage to recycling equipment.
Efficiency in Recycling Operations
The integration of hot melt strap into waste compression and packing processes has significant implications for recycling operations. By enabling more compact and stable waste bundles, hot melt strap optimizes the space utilization within recycling facilities. This not only enhances the overall capacity of these facilities but also reduces the frequency of transportation runs, thereby lowering associated costs and carbon emissions.
Furthermore, the durability and resistance of hot melt strap to environmental factors ensure that compressed waste remains intact throughout the recycling process. This minimizes contamination and maximizes the recovery of recyclable materials, such as paper, plastics, metals, and glass.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
The economic benefits of using hot melt strap in waste compression and recycling are multifaceted. By reducing transportation costs and increasing facility capacity, recycling operations can become more cost-effective. Additionally, the ease of application and removal of hot melt strap translates to reduced labor requirements and operational downtime.
From an environmental perspective, hot melt strap contributes to more sustainable waste management practices. Its ability to withstand moisture and environmental stressors reduces the risk of waste leakage and contamination, preserving the integrity of recyclable materials. Moreover, the thermoplastic nature of hot melt strap means it can potentially be recycled itself, further minimizing waste and promoting circular economy principles.

Conclusion
Hot melt strap stands out as a reliable and innovative tool for waste compression and efficient recycling. Its high tensile strength, moisture resistance, and adaptability make it ideal for securing compressed waste bundles, facilitating easier handling, transportation, and processing. By optimizing space utilization, reducing transportation costs, and minimizing contamination, hot melt strap contributes to more efficient and sustainable recycling operations. As society continues to prioritize environmental stewardship and resource conservation, the adoption of hot melt strap in waste management practices will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in advancing these goals.
In summary, hot melt strap is not just another strapping material; it is a testament to the power of innovation in driving forward the waste management and recycling industries. Its unique properties and applications promise to revolutionize how we handle waste, making the recycling process more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, hot melt strap emerges as a vital component in this journey.